Weight-loss, diabetes drugs linked to vision problems in small study

Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are a popular class of drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. However, a small study conducted at the University of British Columbia has revealed an unexpected side effect of these medications – vision problems.
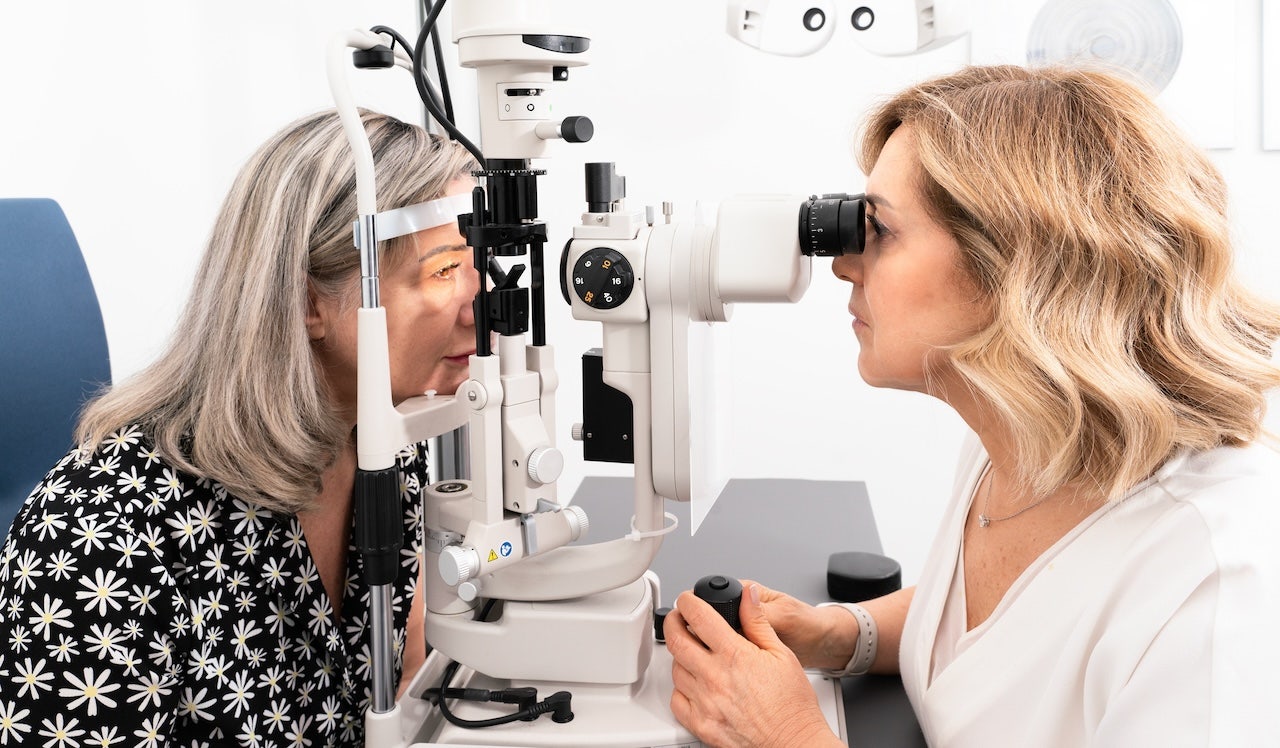
The study included nine patients who were using GLP-1 drugs and developed various ophthalmic complications. Most of the patients had nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), which can cause vision loss in one eye. Other complications included bilateral papillitis and paracentral acute middle maculopathy.
All the patients had a history of type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and/or sleep apnea. Interestingly, one of the patients was using the drugs for weight loss and did not have a prior history of diabetes. In another case, when the drug was stopped and reintroduced, the condition reappeared, suggesting a causal link.
While the study has its limitations, including its small size and lack of a control group, it raises concerns about the potential risks associated with GLP-1 drugs. Ziyad Al-Aly, a clinical epidemiologist at Washington University in St. Louis, emphasized the need for large, controlled studies to evaluate the long-term health effects of these medications, especially regarding eye problems.
Dr. Seth Kipnis, medical director of bariatric and robotic surgery at Hackensack Meridian Jersey Shore University Medical Center, noted that while rare, vision changes from GLP-1 drugs may be related to rapid blood sugar changes rather than the medications themselves. He advised patients to report any unusual symptoms to their prescribing doctors and emphasized the importance of close monitoring for side effects.
Novo Nordisk, the maker of popular GLP-1 drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy, stated that NAION is a rare eye disease and is not considered an adverse drug reaction for their formulations of semaglutide. They recommend that decisions regarding treatment with these medications should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, weighing the benefits against the potential risks.
In conclusion, while GLP-1 drugs have shown benefits for managing diabetes and obesity, the study highlights the importance of monitoring for potential side effects, especially concerning vision problems. Patients should discuss any concerns with their healthcare providers and report any unusual symptoms while taking these medications.